人工智能之父John McCarthy将AI视为科学和工程的结合,而机器学习是AI已经实现的 部分,利用机器学习技术,计算机能够通过体验(数据)来像人类一样学习,而不需要 被显式地编程。这篇文章将详细介绍我们在大作业项目如何使用Python的Keras深度学习框架, 实现一个卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network)来识别图像中的店铺LOGO/招牌。

随着越来越多的数据可用,机器学习现在已经广泛地应用于各个领域,例如个性化的视频 推荐、医疗搜索中的图像和语音识别、欺诈识别、股票市场分析、自动驾驶车辆等等。 我们对于识别图像中的店铺招牌有兴趣的原因之一,在于后续我们将基于这一技术实现 对twitter微博的情感分析。
要快速掌握机器学习应用的开发,推荐汇智网的机器学习系列教程。
1、数据集选择与预处理
任何机器学习项目的第一步,都是找到有趣的数据集。鉴于我们稍后希望将这一技术 应用到twitter微博中的任意图像以分类标牌,因此我们使用了Wild数据集,其中 包含11052个包含大标牌的图像。不过我们没有直接从官网下载这个数据集,而是从 QMUL-OpenLogo数据集中提取了9428个图像。首先我们载入图像,然后使用文件夹名称 标记图像中LOGO的目标分类:
1 | from sklearn.datasets import load_files |
在训练的每一步,使用单独的验证数据集对结果参数进行验证是很有意义的。我们定义了一个 检查点来将验证集上获得的最优权重参数保存下来。最终,在完成训练之后我们将使用另一个 单独的数据集来测试我们的机器学习算法:测试数据集。因此我们将图像数据集拆分为 三部分:训练集、验证集和测试集,然后定义如下的检查点:
1 | from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split |
作为预处理的最后一步,我们将每个图像转换为224 X 224 像素和RGB三个通道,以便将数据 转换为Keras的卷积神经网络需要的格式:6033个训练样本、1509个验证样本、1886个测试样本, 三个数据集的形状均为:(样本数,224,224,3):
1 | from keras.preprocessing import image |
2、CNN识别店铺LOG的原理
在第二步,我们来决定要用的机器学习算法。CNN是通常用于图像分析的一种特殊设计的 神经网络,让我们先看一个简单的神经网络:
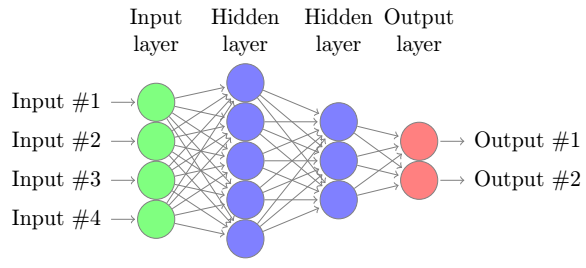
简单地说,神经网络是一个包含输入层、隐层和输出层的图,节点彼此相连。在这里 我们的输入是数据的特征,例如图像中每个像素的RGB值。输出节点对应数据集中的 可能的LOGO分类。不同节点之间的连接有不同的权重,这对应不同的重要性。任何节点 的输出都要使用一个激活函数来处理加权的输入和,就像下面这样:
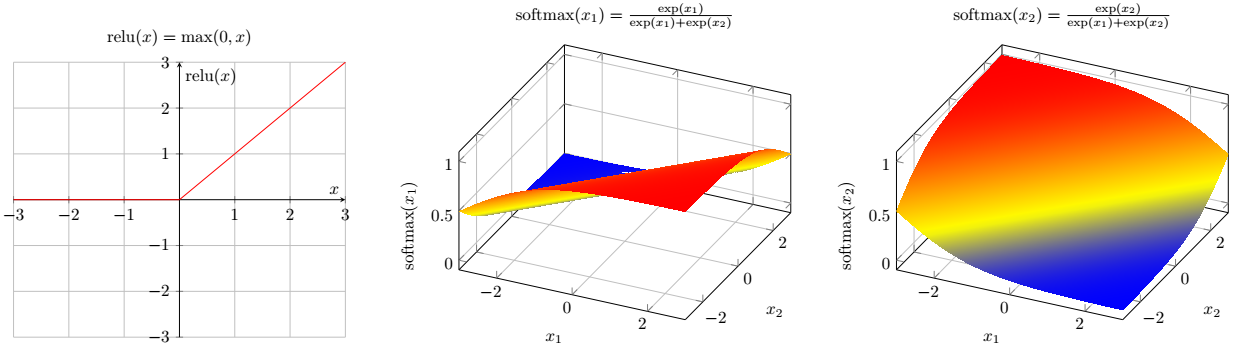
在隐层我们将使用ReLU激活函数,在输出层将使用Softmax激活函数以便将每个输出 节点的值转换到[0,1]区间来获取其概率。当训练神经网络的时候,计算机将不断地优化 神经网络中各连接的权重,以推动网络的输出尽可能接近其真实分类。
当分析图像的时候,经典的神经网络中的参数数量巨大:如果图像大小为224X224像素, 并且我们使用3个RGB值来记录每个像素时,那么我们将需要224X224X3=150528个输入节点, 由于整个网络是全连接的,我们不得不优化数量巨大的连接权重。并且,由于输入节点 被排列为一维向量,神经网络也无法获知图像的任何局部模式。这些问题促成了 卷积神经网络的诞生:

在我们的示例中,输入节点排列为4X4矩阵,然后我们为4个输入区域定义3个2X2的滤波器, 每个区域只连接到隐层对应的3色节点。注意现在3个滤波器定义了3个特征图,每个图用来 检测四个区域中的垂直、水平或对角线之类的特征。在我们的案例中,就是检测出 星巴克、汉堡王或者Telekom的LOGO。
对于3个滤波器而言,由于输入层到卷积层的连接权重参数,因此我们只有2X2X3=12个权重 参数需要优化。当然,在全连接的输出层还有12X9=108个权重参数需要优化。
考虑到我们要识别图像中的小LOGO,CNN的另一个优势就是其具有位移不变性,也就是说, CNN可以识别出图像中任何区域的LOGO。
3、训练Keras卷积神经网络LOGO识别器
我们已经可以开始从零定义我们的卷积神经网络架构了。为此,在上面的卷积层之后,我们 也利用了池化层。池化层有两种常见的类型,都可以缩减特征图的维度:最大值池化和全局平均池化。
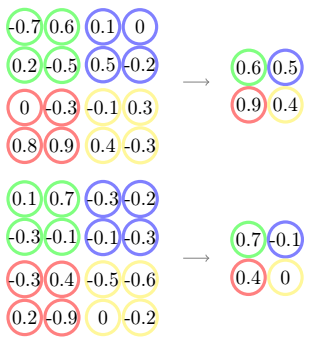
最大值池化层将特征图中的池化窗口映射为最大值。例如,两个特征图的绿色的2X2池化窗口(左侧) 分别映射到最大值0.6和0.7(右侧),容易理解,现在特征图的维度减少到2了。
类似的,一个全局平均池化层将每个特征图映射为其节点的平均值。例如,蓝色特征图的平均值是
-0.1–0.2–0.4–0.1 = - 0.2,可以看到结果特征图中只包含一个节点,因此全局平均池化层可以显著
降低特征图的维度。

现在我们可以定义CNN的架构:
1 | from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, GlobalAveragePooling2D, Dropout, Dense |
最终,我们可以训练CNN模型了。我们选择Adam优化算法,采用交叉熵作为损失函数,使用标准的
衡量指标 准确度 = 正确预测数量 / 所有预测数量。
1 | #Compile the model |
4、模型评估
完成训练之后,我们使用Python的Matplotlib库来绘制训练过程中记录的衡量指标。容易注意到 在训练集上得到的模型准确度在每个epoch之后保持提升,但是在验证集上得到的模型准确度则 徘徊在30%附近:
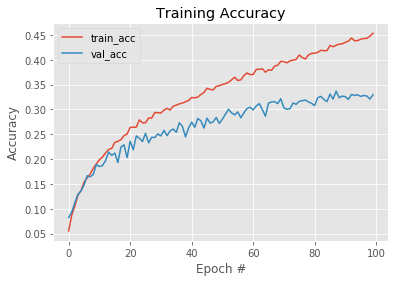
虽然我们在卷积层之后已经增加Dropout层,但模型看起来还是过拟合了,也就是说我们的模型 记住了训练数据,以至于对验证集上没有看到过的数据,效果并不好。
收集更多的训练数据,或者进一步调整学习率、激活函数、节点数量、滤波器数量等架构参数应该 会有一定的作用。但是我们这个项目始终没有获得更好的结果,因此考虑到篇幅问题,我们略去 参数细调部分的说明。
最终,使用cnn_model.evaluate(test_tensors, test_targets, verbose=0),我们的CNN
模型在测试集上达到了31.60%的准确率。
5、使用训练好的模型预测LOGO分类
成功训练好我们的CNN模型后,就可以使用Keras的predict_classes函数预测店铺LOGO的分类了:

原文链接:Classifying Logos in Images with Convolutionary Neural Networks